Please note that some content is only available in Japanese

Metal 3D Printing
Expanding the possibilities of construction 3D printing with metal materials
POINT
-
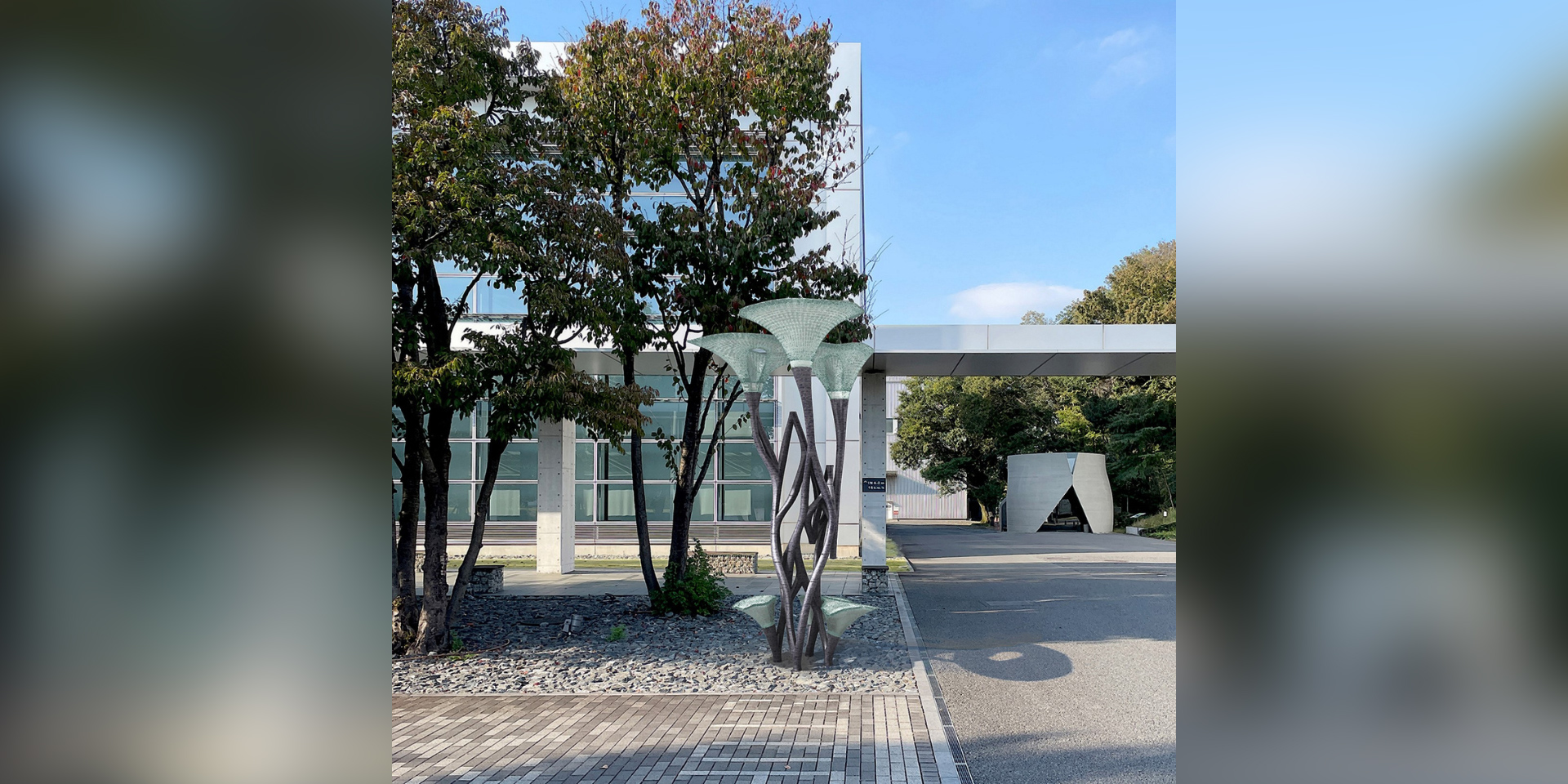
Large-scale mockup created using arc welding-based printing
Introduction video of The brænch
In addition to concrete, we are exploring the use of metal-based 3D printing technologies in the construction field. As a technology demonstration, we used a metal 3D printer based on arc welding (WAAM: Wire & Arc Additive Manufacturing) to fabricate The brænch, a roofed bench-style mockup made by assembling 30 metal pieces of various shapes and sizes.
This technology currently supports small-batch production of diverse components as an alternative to casting, and we are continuing development to expand its applications to a wider range of materials and use cases. -
Achieving slag-free steel component fabrication
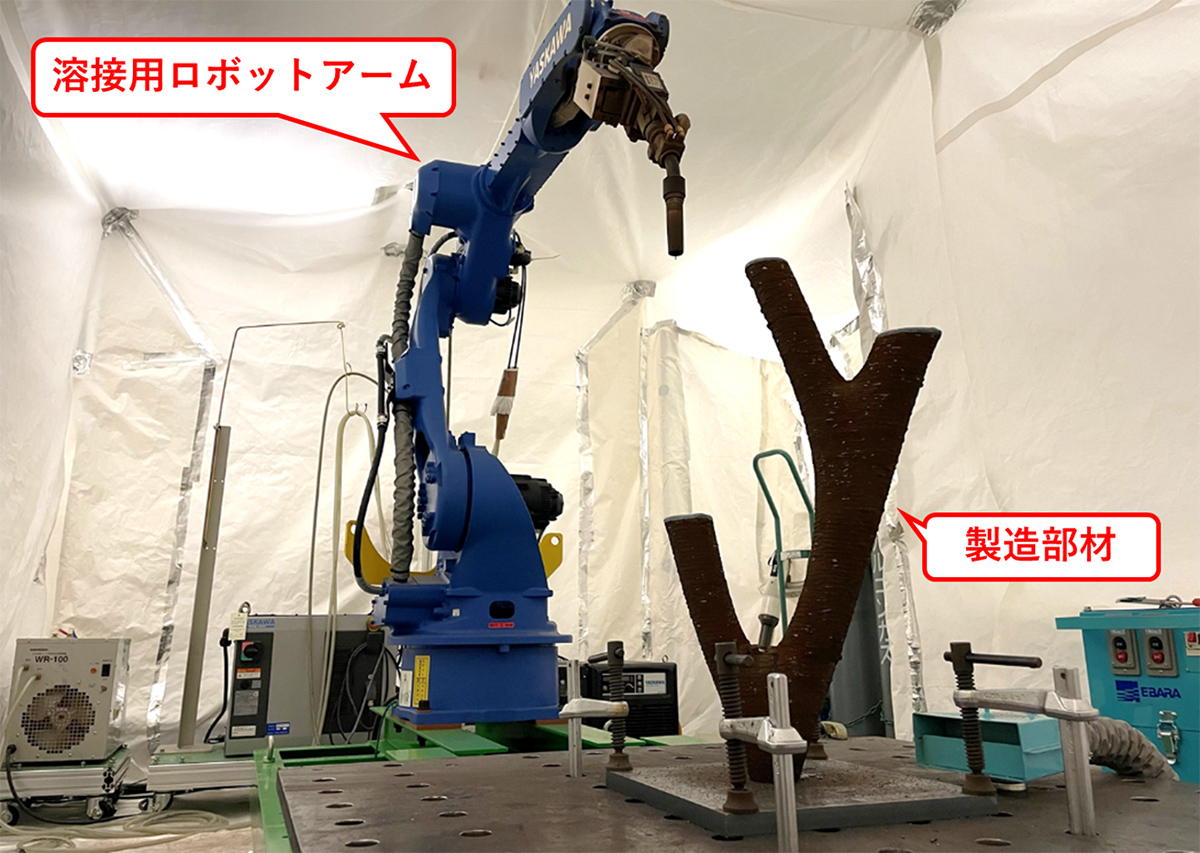
Manufacturing in progress
In wire and arc additive manufacturing (WAAM), using standard steel wire typically results in the formation of slag—non-metallic residue left on welds—which must be removed to prevent degradation in quality and accuracy. However, removing slag layer by layer adds considerable labor, making a slag-free, high-precision, and stable fabrication method highly desirable.
By carefully selecting materials and optimizing welding parameters, we successfully developed a slag-free welding process even when using steel wire. This advancement enables high adaptability to a wide range of needs, as steel is the most commonly used material in the construction industry. -
Fully 3D-printed structure using multiple materials
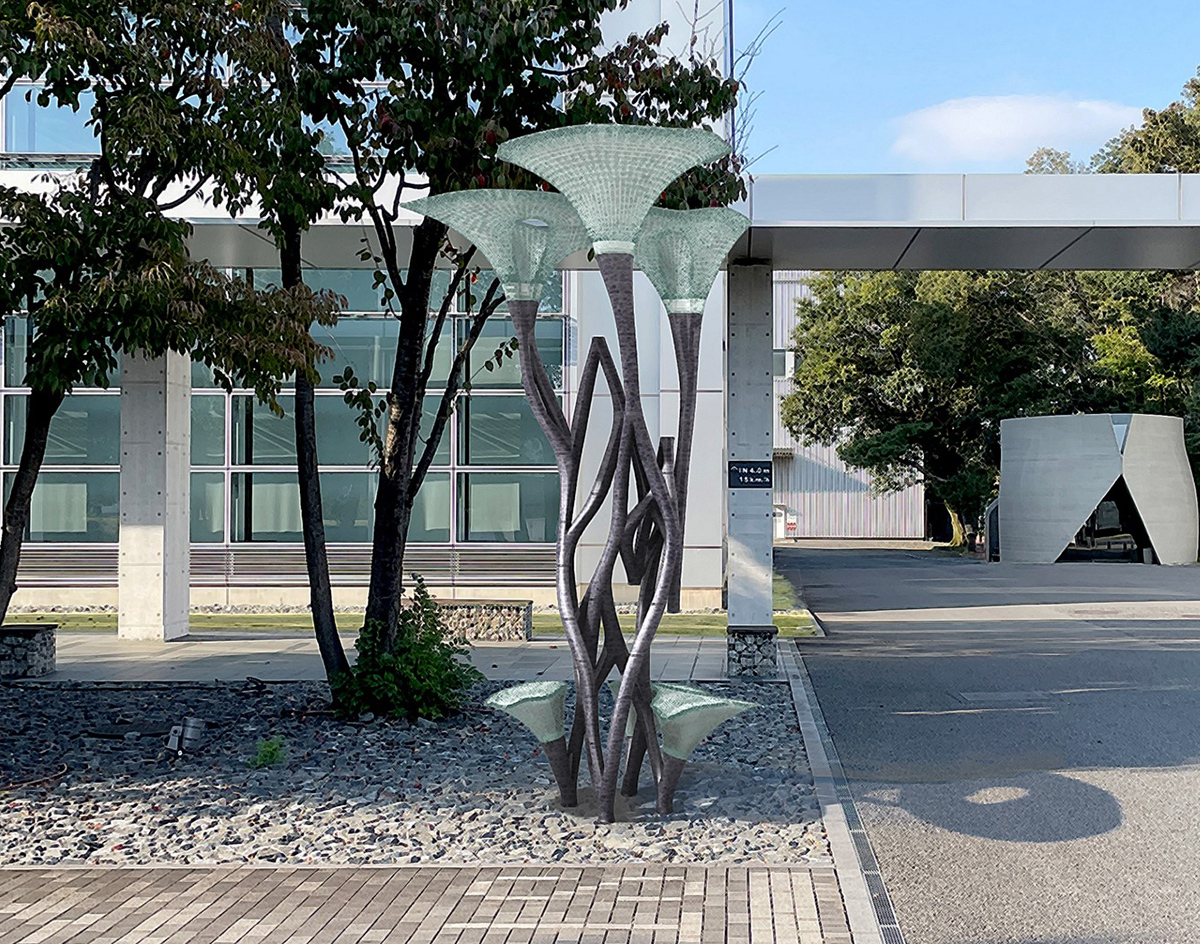

Completed design rendering
The roof and seat of "The brænch" were produced using a 3D printer that uses recycled plastic chips as its ink. Metal components were joined by welding, while resin and metal components were connected with bolts, demonstrating a fully 3D-printed structure combining multiple materials, printers, and joining methods.
